How to Activate Your Data (And Why You Need To)
An overview of data activation and why it's essential.
Feb 29, 2024
By Kelly Kirwan
In the scramble to collect and organize ever-growing volumes of data, organizations across all industries are encountering the same problem: how do we effectively use the data that we’re collecting?
The short answer comes down to investing in the right tools and infrastructure to ensure data is 1.) Properly cleaned, processed, and ready for use and 2.) That data is easily accessible across teams.
So, without further preamble, let’s get into the how-to of data activation.
What is data activation?
Data activation is the process of taking raw data, transforming it into a clean and aggregated format, and then using that data to make informed decisions. Examples of activating data can range from creating personalized audience segments based on demographic or behavioral data (for better ad targeting) to leveraging predictive analytics to understand the likelihood of an event occurring (based on historical data).
Activating data means – in part – that it’s accessible in relevant business applications like an email marketing platform, CRM, or business intelligence tool. Often, businesses store and consolidate their data in a central repository, like a data warehouse or data lake. However, getting data out of these repositories can prove difficult. With a process like reverse ETL, organizations can send data from the warehouse to downstream tools for activation.
4 obstacles that prevent data activation
Data activation can quickly become a complex process: from dealing with fragmented tech stacks, to grappling with identity resolution at scale, to a lack of engineering resources and bandwidth. Below, we list the top four obstacles to look out for when putting together your data activation strategy.
1. Fragmented data infrastructure
Fragmentation occurs when data is scattered across different, siloed systems – like in spreadsheets, a storage system like a data lake or data warehouse, or in the software where it originated.
Because data isn't centralized, it's challenging to draw cross-functional connections and insights. For example, payment data would go to finance and accounting teams, and marketing teams couldn't easily access that information to create a campaign that centers around high-value customers.
2. Inability to tie events to specific customers
Behavioral data is more valuable when you know which customer performs what actions. Say you’re sending a next-purchase recommendation to customers who bought luggage from your store in the last seven days. You might recommend that they buy a carry-on bag next.
But if you learn that one person on your email list called customer service yesterday to complain about a broken handle, you’d want to hold off on sending him that cross-selling message. Instead, you may with the customer success team, and send the person a discounted offer instead to keep their loyalty.
Without the ability to tie events to specific customers, you can’t run personalized experiences. You may even send irrelevant messages that irk customers – and in the process, waste your marketing resources.
3. Unreliable data
It’s risky to make decisions based on data when you can’t be sure of its accuracy.
Say internal dashboards indicate that an e-book is your most effective lead-generation tool. But you don’t realize that your data set contains duplicates – one person actually downloaded the e-book five times, but it was counted as five different customers. This can lead to prioritizing the wrong channels for acquisition, and misunderstanding overall business performance. Unreliable data can stem from a lack of proper naming conventions, no tracking plan, or a lack of real-time data updates (to name a few).
4. Over reliance on technical teams
When non-technical teams completely rely on data engineers or analysts to help build audiences, or understand campaign performance and customer engagement metrics, delays will inevitably occur between an idea, insight, and action.
Especially as businesses grow, if engineers are responsible for manually maintaining the data infrastructure, there will be little to no time for innovation (not to mention the high technical cost of managing ETL pipelines and maintaining data integrity).
Knowing what to build in-house or when to outsource or automate certain processes can be tricky. One way to help businesses decide is to identify the “undifferentiated heavy lifting” that’s necessary but doesn’t contribute to the company’s competitive differentiators. With open-source and API-first platforms, businesses can benefit from certain out-of-the-box features without being completely pigeon-holed into an uncustomizable solution.
For example, the FinTech business ClearScore turned to Segment when they started to think about global expansion. Leveraging Segment’s data collection abilities and seamless integrations allowed ClearScore to free up 25% of engineers’ time. Segment also helps democratize data across, so marketers or customer success agents can autonomously use real-time insights to drive decision-making.
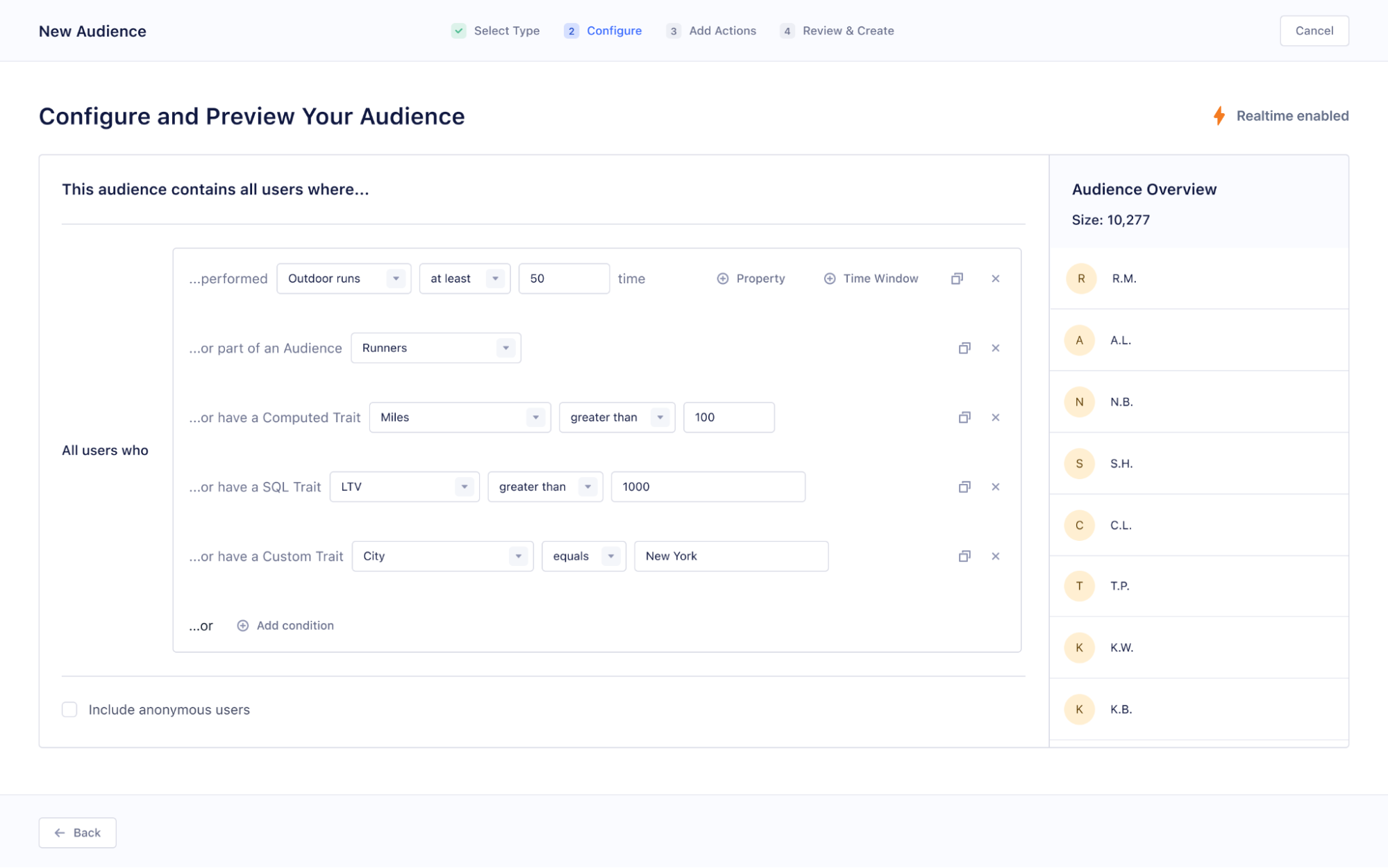
The 3 layers of successful data activation
There are different layers to successful data activation – from ensuring data accuracy to creating nuanced audience segments. Here’s what to keep in mind to ensure you’re using data to its full potential.
Layer 1: Accurate data you can trust
Collecting and cleaning data, in this day and age, is no small task. It often takes a combination of real-time event pipelines, batch processing, building integrations across your tech stack, and ensuring proper data governance is in place. Ensuring data accuracy takes a multi-pronged approach, with key components being:
Establishing a single tracking plan for your organization that details what data you’re collecting, why you’re collecting it, where you’re collecting it from, and where it will be stored.
Create standardized naming conventions for the data you collect, and use automation to enforce those conventions at scale (e.g., automatically blocking data that doesn’t fit your predefined standards).
Prioritizing zero- or first-party data, which is a direct result of customer interactions with your brand.
Implementing privacy guardrails, such as removing or masking personally identifiable information, to comply with global regulations and protect customers.
Layer 2: Identity resolution
Identity resolution is the process of stitching together every interaction a person has with your brand – no matter the channel or device they’re using – into a unified view (e.g, a customer profile). Identity resolution can be complex: what if someone is browsing products on an e-commerce site via their laptop, then on their mobile device via the store’s app, and then creates an account to purchase the items they’d been viewing. How do you attribute all that behavior to the same person?
With identity resolution, you can link previously anonymous user behavior to a known profile after that person is identified in your database.
Layer 3: Personalized omnichannel campaigns
Having a holistic view of customer interactions is fundamental to another important business function: proper segmentation to personalize campaigns and experiences.
You can segment customers based on their behaviors, interests, preferences (and more) to create tailored experiences. Examples of segmentation can range from only targeting prospects in ad campaigns (e.g., suppressing current customers for better ROI) to creating an audience based on their predicted lifetime value.
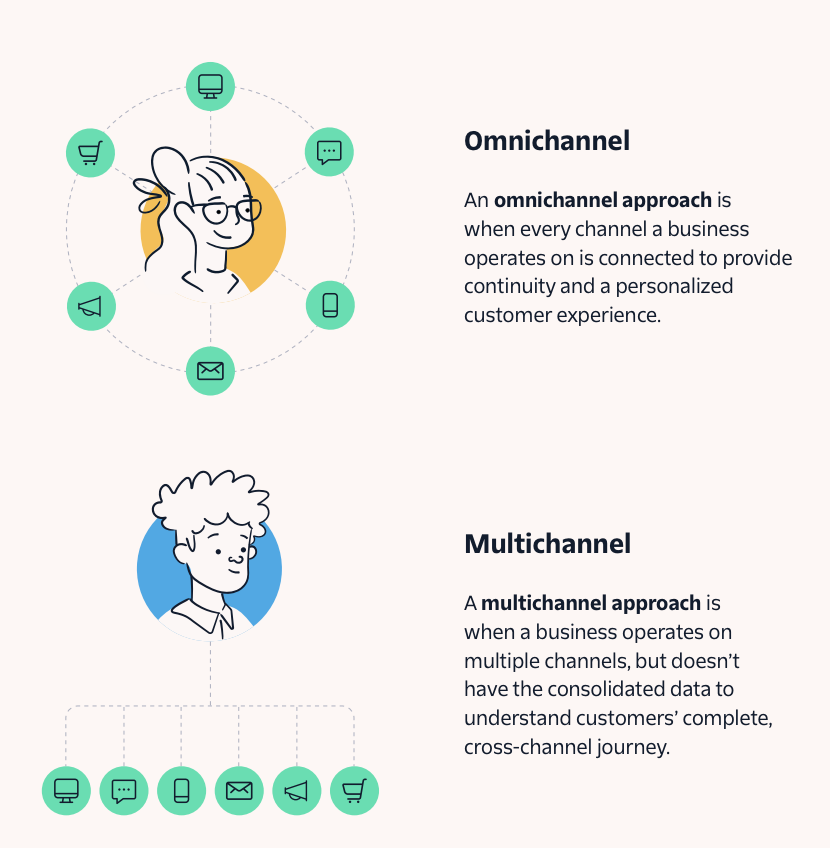
But as we mentioned earlier, people are switching between devices and channels with more ease and fluidity than ever before. This means businesses not only have to know which audience segment they’re targeting, but which channels they’ll be on. Ensuring continuity throughout these cross-channel customer journeys is essential, and a hallmark of omnichannel engagement.
With a combination of real-time event streaming and automation, businesses can actually orchestrate multi-channel experiences that evolve based on a person’s live actions or responses.
How to activate your data with Segment
Segment’s customer data platform helps businesses manage every part of the data lifecycle: from collecting data across touchpoints, to cleaning and consolidating data, and then sending it to downstream tools for activation. (Segment has over 450 pre-built connectors to make this process all the more seamless.)
With reverse ETL, businesses can also better leverage the data stored in their warehouse – syncing it with real-time event streams to enrich customer profiles, and then activating this data in third-party destinations (e.g., using offline data to better target users with ads on Google, TikTok, or Snapchat).
Throughout all these different processes, Segment also ensures that your data is reliable both in its accuracy and delivery. Segment’s Go servers are always ready to receive new data, with a 30ms response time and six nines of availability.
A complete customer view with Segment Unify
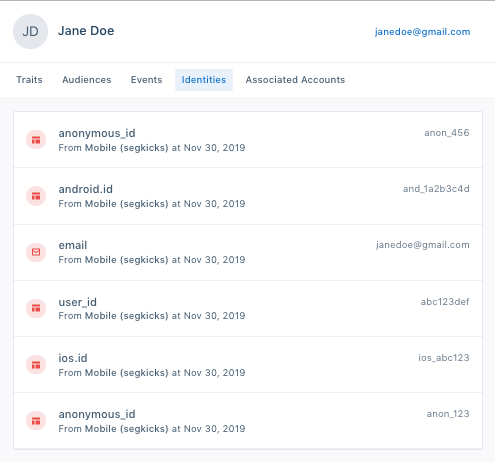
Segment is able to reconcile a customer’s behavior across multiple channels, whether it be mobile, web, or offline touchpoints (like a brick-and-mortar store). Segment aggregates these behavioral events into a single profile for both individual customers and at the account-level. Since our identity resolution is deterministic, that means there’s no guesswork involved when it comes to stitching together user behavior.
And with Segment’s Profile API, you can programmatically view events, traits, and identifiers associated with that profile.
Personalize engagement across channels with Twilio Engage
Twilio Engage allows businesses to engage with customers at the exact right moment, on the right channel, and with the right message. Leveraging real-time data, businesses can build dynamic audiences and customer journeys, which evolve in sync with a person’s behavior (in the moment).
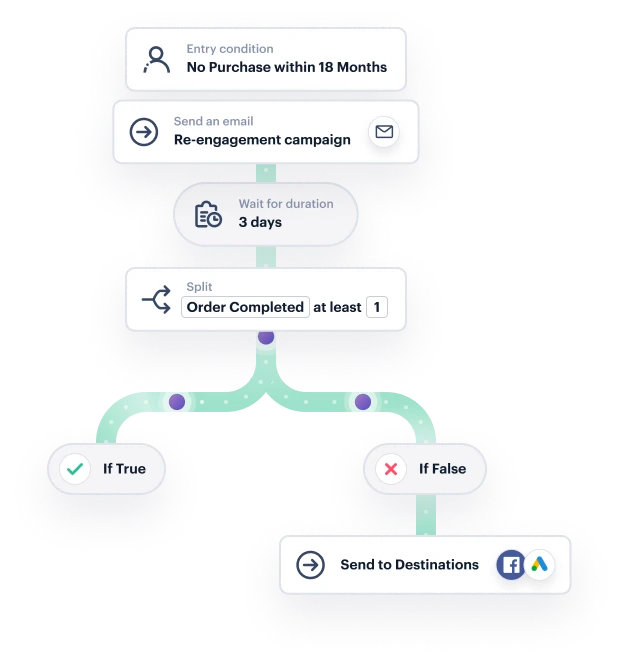
You can then analyze the performance of these omnichannel customer interactions in one central dashboard, to hone in on important insights like the most cost-effective channels for your campaigns.
The State of Personalization 2023
Our annual look at how attitudes, preferences, and experiences with personalization have evolved over the past year.
Get the report
The State of Personalization 2023
Our annual look at how attitudes, preferences, and experiences with personalization have evolved over the past year.
Get the report
Share article
Frequently asked questions
Recommended articles
Data lifecycles in 2024: phases, use cases, & tips
We outline the key data lifecycle stages and explain how understanding them helps teams maximize data value.