What is reverse ETL? A complete guide
Learn how reverse ETL helps businesses activate their data to drive better decision-making and greater operational efficiency.
Learn how reverse ETL helps businesses activate their data to drive better decision-making and greater operational efficiency.
When surveying executives and IT leaders across 12 countries, Seagate and IDC came across a surprising statistic: most enterprises were only using one-third of their data.
The rest was often locked inside a data lake or warehouse, with non-technical teams having limited access and visibility. In a world obsessed with being data-driven and having cutting-edge insights, it seems egregious to have two-thirds of your data remain virtually inaccessible. After all, data can be the pathway to boosting revenue, winning back customers, and streamlining operations. You just have to know how to use it.
To take advantage of the data organizations have collected and stored, they need to make it available in the tools and systems their teams use everyday – which is where reverse ETL comes in.
Reverse ETL is the process of sending data that’s stored in a central repository like a data warehouse to downstream tools and business applications – like a CRM, marketing automation software, or analytics dashboard – for activation.
Reverse ETL helps ensure data is synchronized across all the tools and applications a business uses in its day to day – or in other words, making sure data remains consistent and up to date wherever it’s stored.
You may recognize the acronym ETL, which stands for “Extract, Transform, and Load.” ETL is the process of collecting data from various sources, cleaning and structuring it to match its target destination (i.e., transformation), and then loading it into a repository like a data warehouse. (There’s also the option to load data into a repository like a data lake before transformation takes place, in a process called “ELT.”)
A simple way to think of the difference between ETL and reverse ETL is that they represent two sides of the street, with traffic moving in different directions. ETL is focused on moving data into the warehouse for consolidation and enrichment. Reverse ETL is concerned with taking that cleaned, enriched data out of the warehouse and moving it into downstream tools for team-wide use.
Now that we’ve given an overview of reverse ETL, let’s get into the mechanics of how it works.
Step One: Extraction. This involves querying your data warehouse (e.g., via SQL) to extract the specific data that you need.
Step Two: Transformation. The data that you extract will be in a specific format (data warehouses typically store structured data). So, you may need to transform data so that it matches its target destination. This is where data mapping is pivotal, to trace the movement of data between storage systems and tools into specific fields.
Step Three: Loading. This is when data is loaded into its target destinations. This can be done via an API integration, manual upload, batch processing, or in real time.
Step Four: Activation. Once data is loaded into downstream tools and applications, it can be leveraged by internal teams and even trigger specific actions (e.g., launching a personalized customer interaction based on their recent online and offline behavior).
Step 5: Ongoing Monitoring. As with any process, it’s important to continuously check for quality. Many reverse ETL tools are able to automatically flag failed syncs or errors to help investigate issues.
When we talk about reverse ETL, we tend to focus on four components:
Source: This is where data originated from, which could be a website, cloud application, mobile SDK, etc.
Models: This refers to SQL queries that define and specify which data sets you want to synchronize with downstream tools.
Destinations: These are the tools and applications you want to deliver data to from the data warehouse.
Mapping: This is when you map data from your warehouse to specific fields in your target destinations.
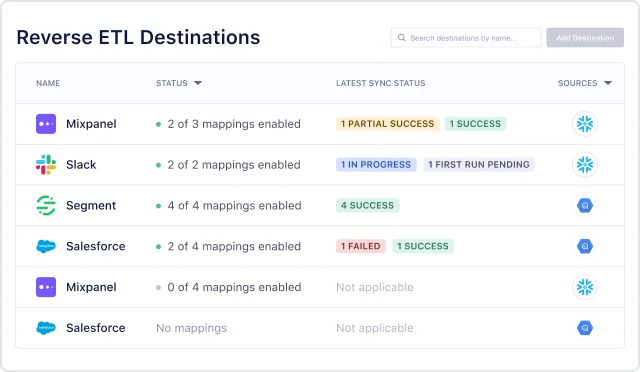
Reverse ETL allows businesses to access and act upon enriched data for better decision-making, customer personalization, and cross-functional collaboration.
“Operationalization” doesn’t just mean using something. In scientific research, it means making an abstract concept concretely measurable.
In the same way, data that sits in a warehouse has a vague potential to contribute value to your business. But when you use it in business apps or tools, you turn it into a central component of marketing campaigns, product development, or business planning.
All departments in a company can operationalize data. For example, finance can create a custom payment plan for B2B customers and sends automated follow-up emails using an invoice and accounting software. Or customer support can automatically prioritize incoming requests or tickets based on someone’s payment tier (e.g., premium users) or lifetime value.
Reverse ETL prevents data from being locked inside its repository. It helps empower internal teams with holistic data sets, rather than limiting them to the data that they can access in their owned tools (e.g., product teams are given a list of high-value customers and give them beta access to a new feature in their SaaS app).
As a result, reverse ETL helps break down data silos and make enriched data sets more accessible across an organization (rather than relying solely on engineers or analysts to manually pull data).
Integrate a reverse ETL tool with operational analytics software to get concrete answers to questions like:
What is the best predictor of customer churn?
What traits and behavioral patterns do customers with the highest lifetime value have in common?
How does the user onboarding experience affect customer loyalty?
What does the customer journey of a certain audience segment look like?
Which communication channel has higher engagement?
Does our product recommendation algorithm lead to larger basket sizes?
To answer questions like these, you need data from multiple channels and departments. And as your business grows, you want to continue asking and answering data-driven questions without having to set up new analytics workflows. Reverse ETL tools make that possible as you only need to integrate them once with your business intelligence and analytics software.
Before going ahead with reverse ETL there are a few things to consider, from team bandwidth to data volume and then the pricing structure of tools.
The World Economic Forum estimates that by 2025, 463 exabytes of data will be generated daily across the globe. As data volume continues to increase at an exponential rate, businesses need to consider the amount of data they’ll need to extract from their warehouse to send to downstream tools, and how regularly they’ll need to do this to ensure synchronicity. On top of that, pricing for reverse ETL tools can be tied to data volume, so it’s important to consider this as well.
Implementing reverse ETL can be a complex process, for a multitude of reasons. When trying to determine just how complex this will be, consider the following:
Your different data sources, how data is formatted, and how you’ll make this data compatible with your reverse ETL tool and its target destinations.
How you’ll handle and resolve data inconsistencies to ensure quality at scale.
If the reverse ETL has pre-built integrations with the tools in your tech stack (to help streamline setup). .
How you’ll protect data throughout the extraction and transformation process (something that’s especially important if you’re in a business that deals with personally identifiable information, like healthcare).
Being able to implement reverse ETL at scale is another important factor to consider. Think of the impact that the reverse ETL process could have on your system resources, network bandwidth, and processing capabilities, especially if you’re working with large volumes of data.
With Twilio Segment, businesses are able to harness reverse ETL alongside all the capabilities of a complete customer data platform like real-time identity resolution, profile portability, and automated data governance.
As a result, businesses can enrich their identity-resolved customer profiles in the data warehouse before syncing them with downstream tools for activation.
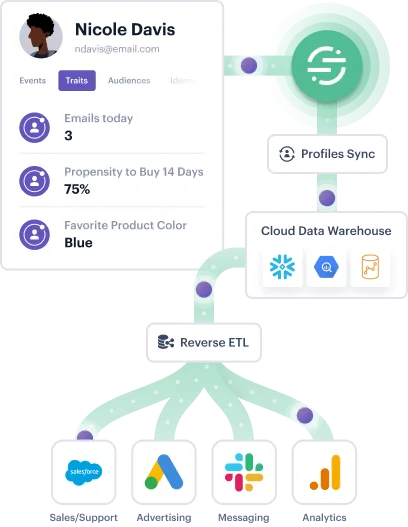
A key benefit of this is that Segment provides every type of a data pipeline in one platform (e.g., event streaming, ETL, reverse ETL) – meaning businesses don’t need to look to multiple different vendors to orchestrate and manage their data.
Segment’s flexibility and pre-built connectors also make it seamless to integrate into businesses’ tech stack, reducing implementation time.
Examples of use cases that can be done with Twilio Segment’s reverse ETL include:
It’s free to connect your data sources and destinations to the Segment CDP. Use one API to collect analytics data across any platform.
ETL (extract, transform, load) is the process of collecting data from sources, cleaning and structuring it, and loading it into a repository like a data warehouse or data lake. You may also load the data before transforming it (ELT). In reverse ETL, you copy data from a data warehouse or data lake, transform it, and load it into business SaaS applications.
Sales, marketing, customer support, and revenue operations are common use cases for reverse ETL.
Reverse ETL lets you activate data in the tools and apps that teams use every day, so you can create highly personalized experiences and make strategic decisions. Reverse ETL tools prevent data silos, scale up your analytics, and reduce the time data teams spend manually extracting and preparing data.
Implementing reverse ETL is not without its challenges, which include but are not limited to: 1. Complexity. It can quickly become an intricate process to map data from its storage systems to target destinations, and ensure that data is properly formatted in both locations. 2. Volume. Data is being generated at a rate never before seen, and businesses have to consider how much data they will need to extract, transform, and load, and how often. 3. Data quality. Throughout the reverse ETL process, it’s important to ensure data remains valid, which includes flagging any potential errors or inconsistencies before they reach target destinations. 4. Security. Protecting customer data is essential for every business, and especially for highly regulated industries like healthcare that are held to HIPAA compliance. Ensuring that data has the right access controls and is encrypted while it's synced to external systems is a must.
Yes, reverse ETL can enable real-time data integration (i.e., ensuring data is synchronized and continuously up to date across the tech stack). To do this, the reverse ETL tool needs to detect changes in the data warehouse or source data (e.g., via API notification, event-based triggers, etc.) and should have protocols in place to handle data transformations and error detection. A few other factors will impact a reverse ETL tool’s ability to perform real-time data integration, like low latency connections and the data’s complexity.